Human Reproduction class 12 Short notes for neet || questions of human reproduction
The Human Reproduction topic generally holds minimum 20+ marks in every NEET/ AIIMS/ JIPMER exam.
It is equally important for the students who are sitting on the board exams this year. The topic generally starts with a detailed explanation of male and female reproductive systems. This is one topic from which at least one diagrammatic question is asked for the NEET exam.
Here when I am discussing this topic with you I’ll also be explaining in short some of the terms for quick revision purpose. But you all will have to go through these terms and terminology in detail for your preparation. I’ll also attach some questions from previous year papers so that you realize the connection to these topics.
Human Reproduction Notes
Now we’ll be discussing the 10 important topics from Human Reproduction from NEET point of view.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
Although it is a very vast topic to discuss, there are a few very important topics of which questions have been asked repeatedly:
The flow of sperm from testes to outside
Seminiferous tubules → Rete testis→ Vas efferentia→ Epididymis →Vas deferens → Ejaculatory duct → Urethra
Functions and locations of male accessory glands
- Seminal Vesicles
- Prostate gland
- Bulbourethral gland
Hormonal control of male reproductive system
GnRH is secreted by the hypothalamus. It stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH. In males, LH is called Interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH) it secretes androgens. Testosterone is the principal androgen. FSH stimulates Sertoli cells of the testis to secrete an androgen-binding protein that concentrates testosterone in seminiferous tubules. Inhibin is also secreted by the same Sertoli cells.
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
The most important parts of female reproductive system are-
- The study of Section of mammalian ovary showing follicular maturation
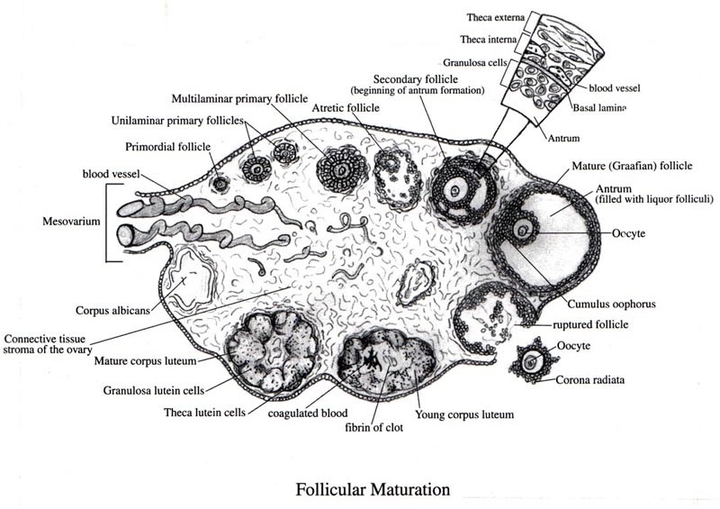
- Structure of Graffian follicle
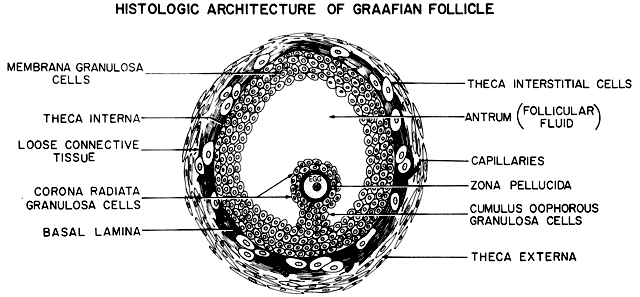
- Hormonal control of female reproductive system
GnRH is secreted by the hypothalamus. It stimulates the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland to secrete LH and FSH. FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles. LH stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete progesterone. The rise in the level of progesterone inhibits the release of GnRH.
PYQ: Yellow coloured corpus luteum degenerates to form ________, when egg formation does not take place.
- Corpus bigemina
- Corpus quadrigemina
- Corpora albicans
- Corpora callosum
PYQ: Which of the following layers in an antral follicle is acellular? [AIPMT 2015]
- Granulosa
- Theca interna
- Stroma
- Zona pellucida
SPERMATOZOON (Sperm)
- The structure of Spermatozoon is as important as its parts- consisting of
- Acrosomal Head,
- Neck which contains the proximal centriole towards the nucleus and distal centriole which gives rise to axial filament.
- Middle piece contains the mitochondrial coiled round the axial filament called mitochondrial spiral.
- Tail which is several times longer than the head and helps in locomotion.
- Sequence of sperm formation
PYQ: The correct sequence of sperm formation is- [AIPMT 2013]
- Spermatogonia→Spermatozoa→Spermatocyte→Spermatid
- Spermatogonia→Spermatocyte→Spermatid→Spermatozoa
- Spermatid→Spermatocyte→Spermatogonia→Spermatozoa
- Spermatogonia→Spermatocyte→Spermatozoa→Spermatid
PHASES OF OOGENESIS AND HORMONAL CONTROL OF OOGENESIS
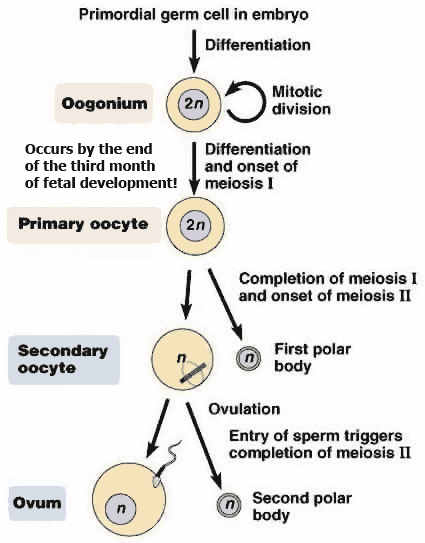
- Study the functions of LH and FSH
- Questions are asked related to the polar bodies.
HORMONAL CONTROL OF MENSTRUAL CYCLE
Different phases of Ovulation are controlled by different hormones during the menstrual cycle
- Menstrual phase is caused by the reduction of progesterone and estrogen.
- Proliferative phase is caused by the increased production of estrogen.
- LH causes ovulation
- Secretory phase is caused by increased production of progesterone.
PYQ: Which of the following events is not associated with ovulation in human females?
- Decrease in oestradiol
- Full development of Graffian follicle
- The release of the secondary oocyte
- LH surge
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL EVENTS OF FERTILIZATION
You should have an idea of certain processes and reactions taking place in this event like-
- Acrosomal Reaction- This includes some chemicals of which you should have an idea of their function like- i) hyaluronidase ii) corona penetrating enzyme iii) zona lysine
- Cortical reaction
- Cone of Reception or Fertilization cone
- Karyogamy
PYQ: Cortical granules are associated with
- Spermatogenesis
- Oogenesis
- Fertilization
- Cleavage
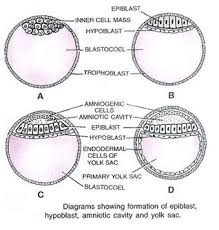
GASTRULATION
- Formation of embryonic disc
- Formation of the amniotic cavity
- Formation of Chorion and Amnion
- Formation of Yolk sac
- Types of cleavage-
- Holoblastic
- Meroblastic
- Determinate
- Indeterminate
FUNCTIONS OF PLACENTA
- Questions have been asked from this topic in the form of the odd one out, so one should know the important functions of the placenta. Just for your quick revision here are the few important functions of the placenta.
- Nutrition to the fetus.
- Respiration
- Excretion
- Storage of glycogen, fats etc.
- As a barrier
- Endocrine function- Placenta secretes some hormones like estrogen, progesterone, hCG, hCS, relaxin.
- Functions of hormones like hCG( Human chorionic gonadotropin), hCS (Human chorionic somatomammotropin)
PARTURITION
- Meaning of the term Parturition
- Process and the terms related to it, like- Foetal ejection reflex, Labour pains, Corticotropin-releasing hormone, dilation stage, placental stage or after birth.
DEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
Few terms are on and off seen in medical exams related to disorders of fetal development. The important ones for a quick glance are-
- Amnionitis- Inflammation of amnion usually resulting in premature rupture of amnion.
- Abortion-It is giving birth to an embryo or fetus before the completion of 20 weeks of gestation.
- Teratogeny- Production of the malformed infant.
Thanks
Team
Go . Score Better.


Comments
Post a Comment